First-in-class targeted treatment
TAVNEOS® is the only targeted therapy for AAV (GPA/
MPA)1* to address a key driver of vascular
inflammation in the alternative complement pathway2,3
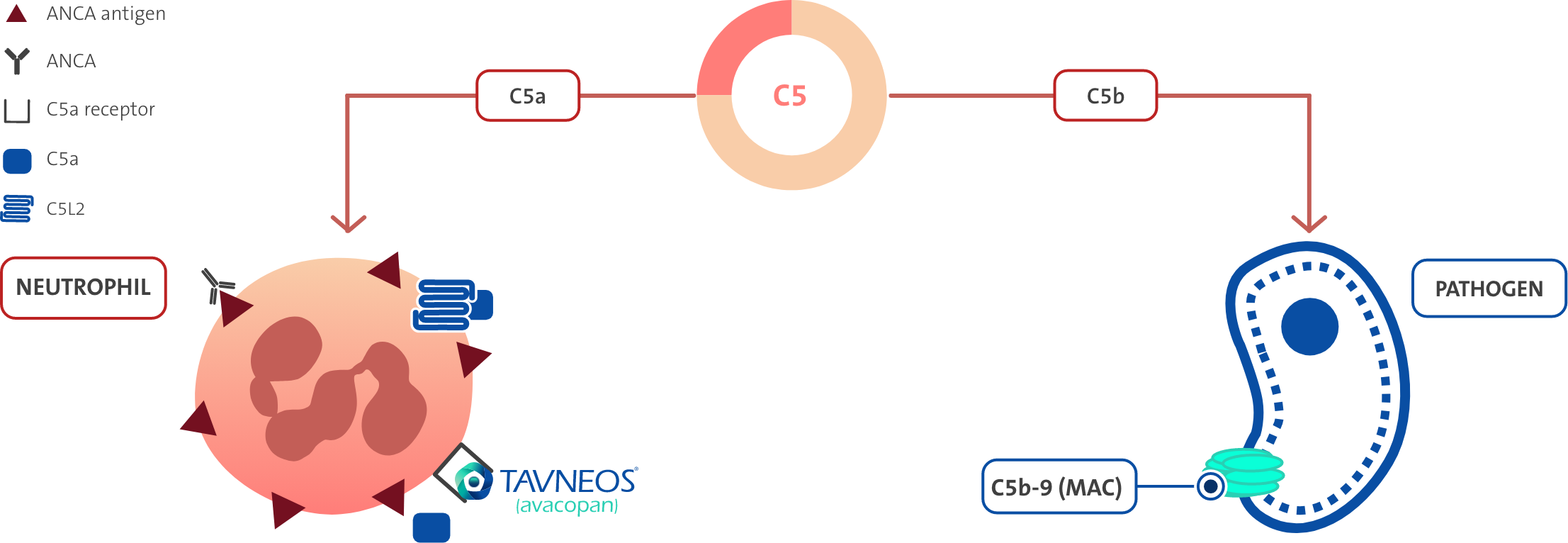
TAVNEOS® reduces the pro-inflammatory effects of C5a, including:2
- Neutrophil activation and migration
- Adherence to sites of small blood vessel inflammation
- Vascular endothelial cell retraction and permeability
TAVNEOS® does not block the production of C5b, which is essential for the formation of the membrane attack complex (MAC)2
Activation of the alternative complement pathway plays a key role in AAV, and no established therapies address this key driver of vascular in ammation2,4,5-10
Already recommended by EULAR 2022
The EULAR recommendations for the management of ANCA-associated vasculitis: 2022 update, recognised the ability of a TAVNEOS®-based regimen to improve disease control, and the potential to lower GC toxicity and improve renal function10,11
EULAR 2022 RECOMMENDATION LEVEL OF EVIDENCE 1b:
TAVNEOS (avacopan) in combination with RTX or CYC may be considered for induction of remission in GPA or MPA, as part of a strategy to substantially reduce exposure to GCs10
Consider TAVNEOS® in subgroups likely to have enhanced benefit vs GC therapy:10
- patients at risk of development or worsening of GC-related adverse effects and complications
- patients with active glomerulonephritis and rapidly deteriorating kidney function
No data on the use of TAVNEOS® beyond 1 year, so longer-term use cannot be recommended10
In ADVOCATE, remission was sustained to Week 52 (primary endpoint) at a higher rate in the TAVNEOS®-based regimen (65.7%) vs GC-based regimen (54.9%) so TAVNEOS® appears to have efficacy for maintenance of remission 10

 Please rotate your device
Please rotate your device
Understand more about the pathogenesis of AAV and how TAVNEOS® works
*TAVNEOS®, as an adjunctive treatment to standard immunosuppressive treatment that includes rituximab or cyclophosphamide with glucocorticoids, is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with severe, active ANCA-associated vasculitis (GPA/MPA).12
AAV, ANCA-associated vasculitis; ANCA, anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody; C5a, complement component 5a; C5aR, C5a receptor; C5b, complement component 5b; C5L2, C5a receptor-like 2; EULAR, European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology; GC, glucocorticoid; GPA, granulomatosis with polyangiitis; MAC, membrane attack complex; MOA, mechanism of action; MPA, microscopic polyangiitis.
References
1. EMA. First-in-class medicine recommended for treatment of rare blood vessel inflammation. Nov. 2021. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/news/first-class-medicine-recommended-treatment-rare-blood-vessel-inflammation. Date Accessed: October 2023. 2. Bekker P, et al. PLoS ONE 2016;11(10):e0164646. 3. Thurman JM, Holers VM. J Immunol 2006;176(3):1305–10. 4. Hutton HL, et al. Semin Nephrol 2017;37(5):418–3. 5. Jennette JC, Nachman PH. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2017;12(10):1680–91. 6. Al-Hussain T, et al. Adv Anat Pathol 2017;24(4):226–34. 7. Lamprecht P, et al. EMJ Rheumatol 2021;8(1):36–42. 8. Liberman AC, et al. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2018;9:235. 9. Nozaki Y. Front Immunol 2021;12:631055. 10. Hellmich B, et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2023;0:1–18. 11. Jayne D, et al. N Engl J Med 2021;384(7):599–609. 12. TAVNEOS® Fachinformation, www.swissmedicinfo.ch.


 Scroll down
Scroll down